Superset - Developer Guide
Learn how to install and configure Apache Superset on AWS with our step-by-step deployment guide. This comprehensive resource walks you through provisioning your cloud environment, securely deploying Superset, and optimizing it for scalability, high availability, and performance on AWS. Whether you’re building interactive dashboards, running complex analytics, or managing large-scale data visualizations, this guide will help you set up and run Superset efficiently in the cloud.
Welcome to the Superset Deployment Guide for AWS Integration! Unlock the full potential of Apache Superset, the open-source business intelligence and data visualization platform. Seamlessly integrate with your AWS infrastructure to achieve enterprise-grade scalability, secure access, and DevOps-friendly automation. Empower your teams with interactive dashboards, real-time analytics, and extensibility for mission-critical insights. Let’s get started and elevate your data visualization and decision-making with Superset on AWS.
Prerequisites
Before you get started with the Superset AMI, ensure you have the following prerequisites:
- Basic knowledge of AWS services, including EC2 instances and CloudFormation.
- An active AWS account with appropriate permissions.
- Enough vCPU limit to create an instance (Follow https://meetrix.io/articles/how-to-increase-aws-quota/).
Launching the AMI
Step 1: Find and Select Superset AMI
- Log in to your AWS Management Console.
- Navigate to the 'Superset' in AWS Marketplace.
Step 2: Initial Setup & Configuration
- Click the "Continue to Subscribe" button.
- After subscribing, accept the terms and click "Accept Terms".
- Wait a few minutes until processing completes, then click "Continue to Configuration".
- Select "CloudFormation script to deploy Superset" as the fulfillment option and choose your region. Click "Continue to Launch".
- From the "Choose Action" dropdown, select "Launch CloudFormation" and click "Launch".
Create CloudFormation Stack
Step1: Create a stack
- Ensure the "Template is ready" option is selected under "Prepare template".
- Click "Next".
Step2: Specify stack options
- Provide a unique "Stack name".
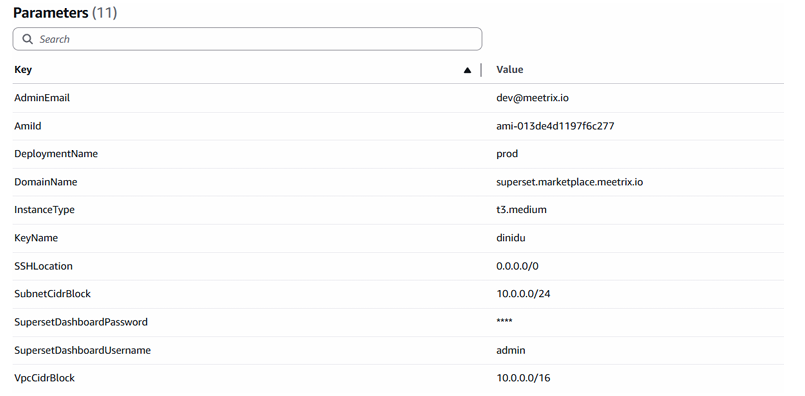 Provide the "Admin Email" for SSL generation.
Provide the "Admin Email" for SSL generation.- Enter a value for "DeploymentName".
- Provide a public domain for "DomainName". Superset will automatically try to set up SSL if the domain is hosted on Route53. If unsuccessful, you must set up SSL manually.
- Choose an instance type "InstanceType" (Recommended: t3.medium).
- Enter Superset username for login.
- Enter Superset password for login.
- Select your preferred "keyName".
- Set "SSHLocation" to 0.0.0.0/0.
- Keep "SubnetCidrBlock" as 10.0.0.0/24.
- Keep "VpcCidrBlock" as 10.0.0.0/16.
- Click "Next".
Step3: Configure stack options
- Choose "Roll back all stack resources" and "Delete all newly created resources" under "Stack failure options".
- Click "Next".
Step4: Review
- Review and verify the details you've entered.
- Tick "I acknowledge that AWS CloudFormation might create IAM resources with custom names".
- Click "Submit".

Afterward, you'll be directed to the CloudFormation stacks page. Please wait for 5-10 minutes until the stack has been successfully created.
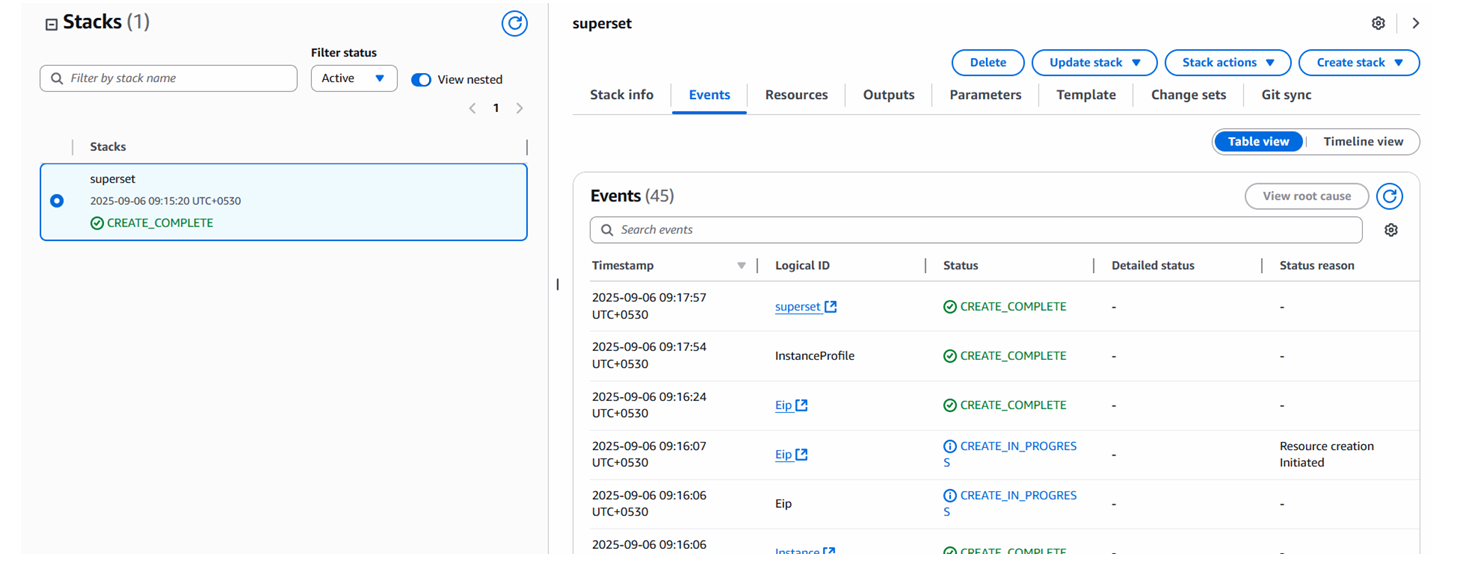
Update DNS
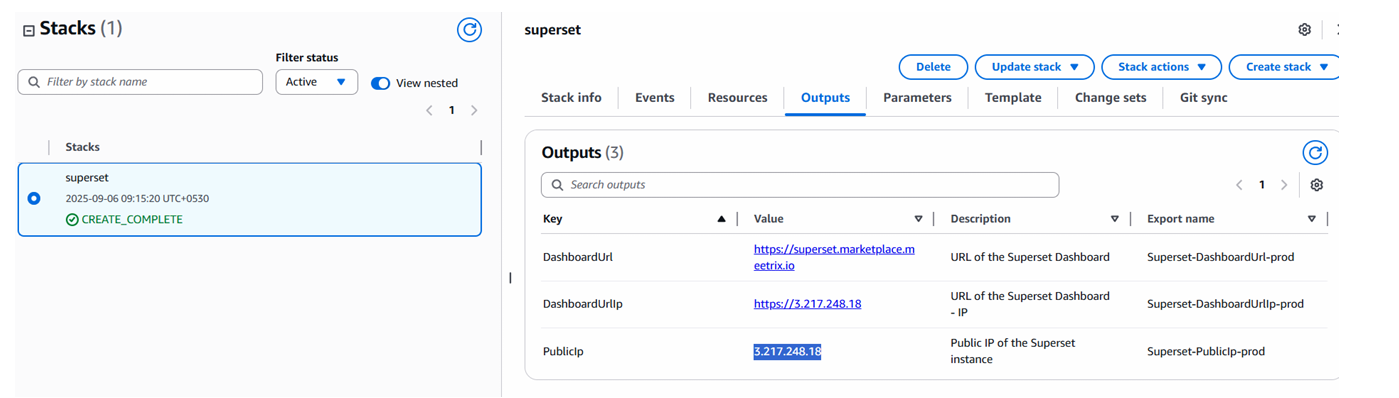
Step1: Copy IP Address
Copy the public IP labeled "PublicIp" in the "Outputs" tab.
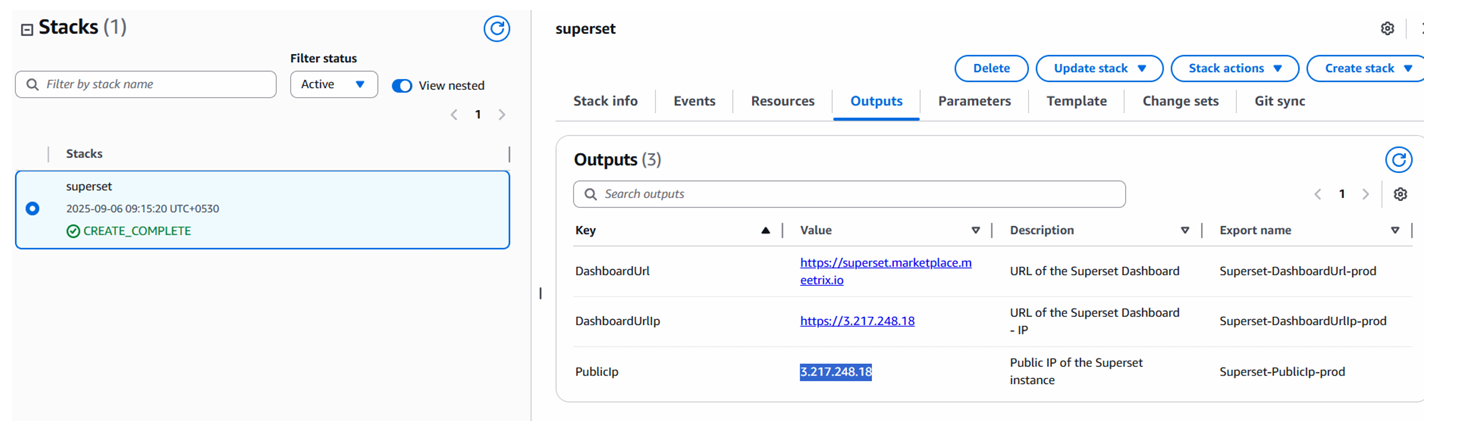
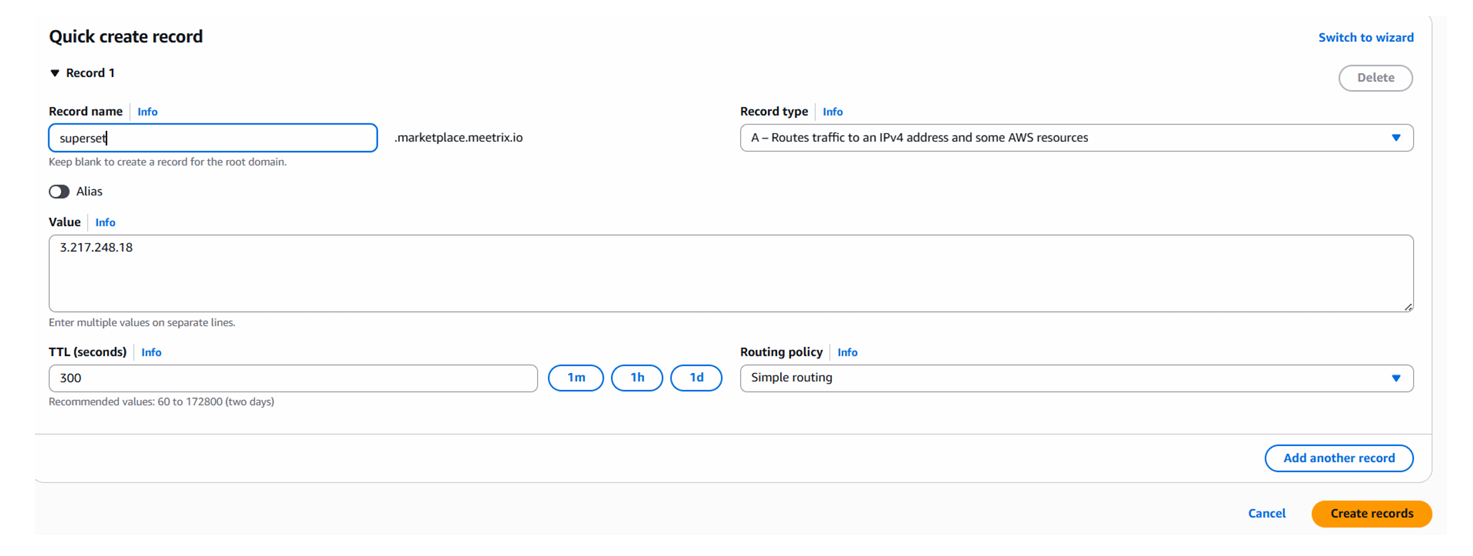
Step2: Update DNS
- Go to AWS Route 53 and navigate to "Hosted Zones".
- Click Create record.
- Add a record name and paste the copied PublicIp into the value textbox.
- Click "Save".
Access Superset
Access Superset using the "DashboardUrl" or "DashboardUrlIp" provided in the Outputs tab.
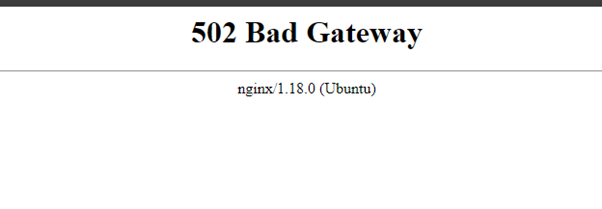
Note: If you receive a “502 Bad Gateway” error, wait approximately 5 minutes and refresh the page. The application may still be initializing.
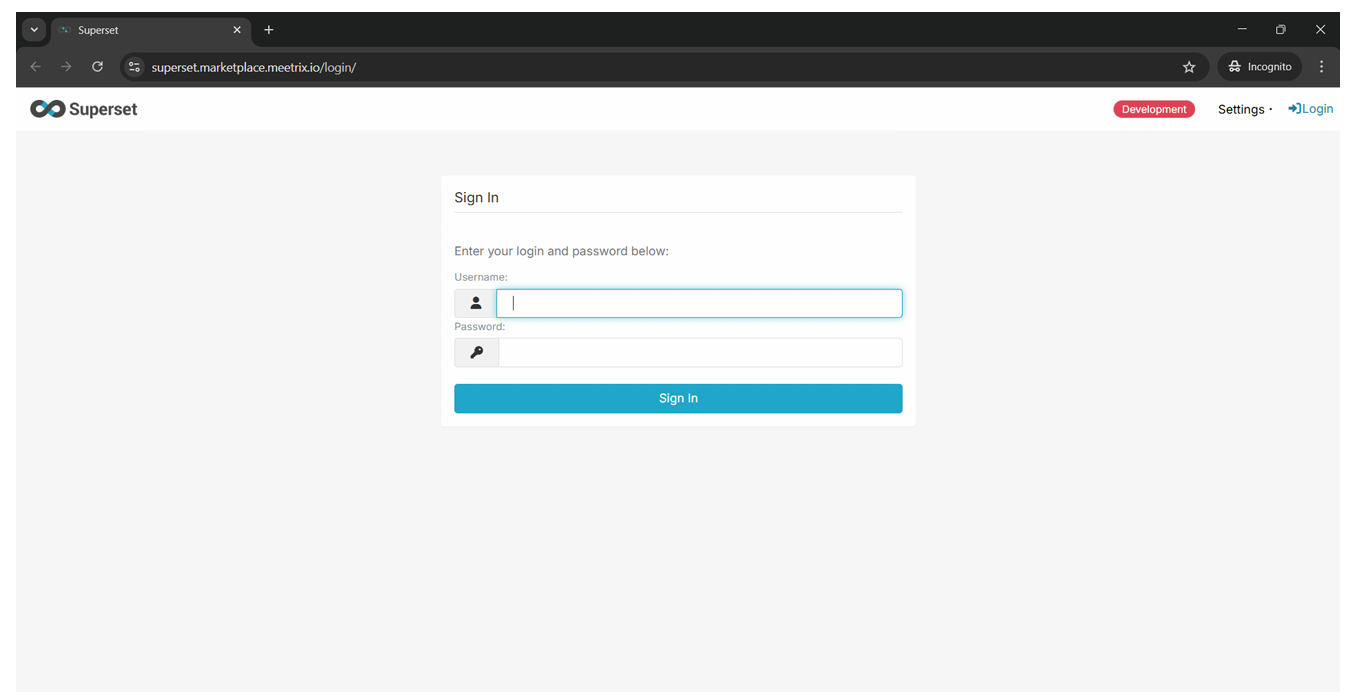
Please enter the Username and Password that you provided during stack creation. Store them securely for future reference.
Generate SSL Manually
Superset will automatically try to set up SSL when a Route53-hosted domain is provided. If it fails, follow these steps to generate SSL manually.
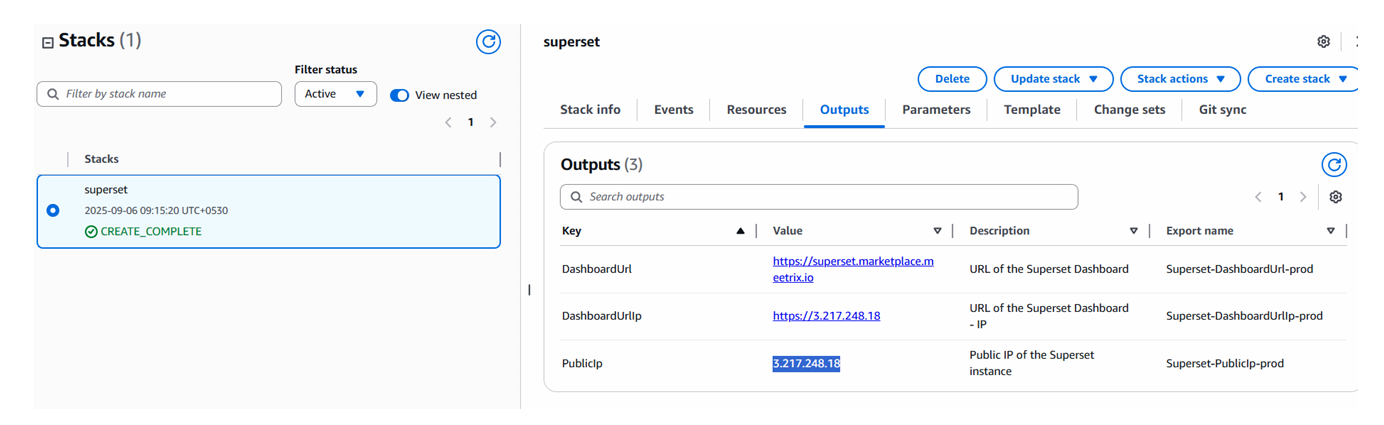
Step1: Copy IP Address
- Follow the Update DNS steps above, if not already done.
- Copy the Public IP indicated as "PublicIp" in the "Outputs" tab.
Step2: Log in to the server
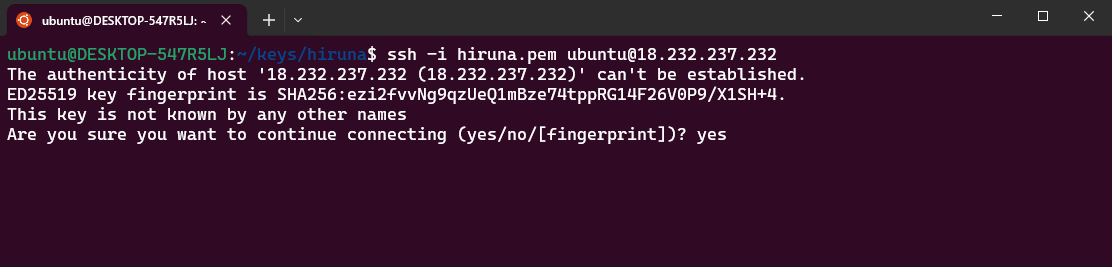
- Open the terminal and go to the directory where your private key is located.
- Run: ssh -i <your key name> ubuntu@<Public IP address>
- Type "yes" and press Enter to confirm.
Step3: Generate SSL
Run the following command and follow the prompts:
sudo /root/certificate_generate_standalone.shCheck Server Logs
Step1: Log in to the server
ssh -i <your key name> ubuntu@<Public IP address>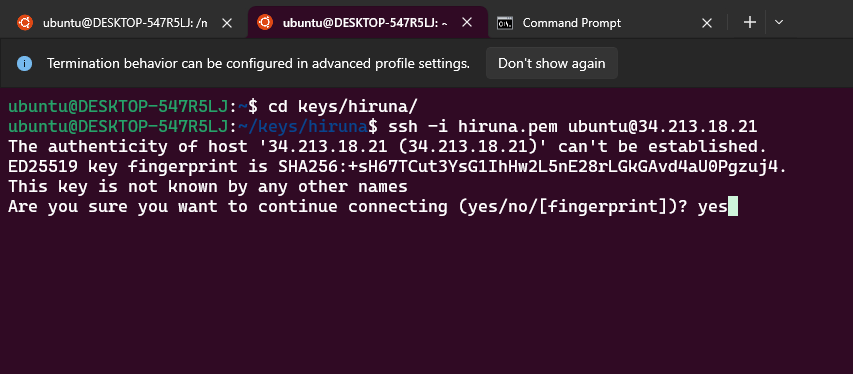
Step2: Check the logs
sudo docker ps
sudo docker logs <container-id-prefix>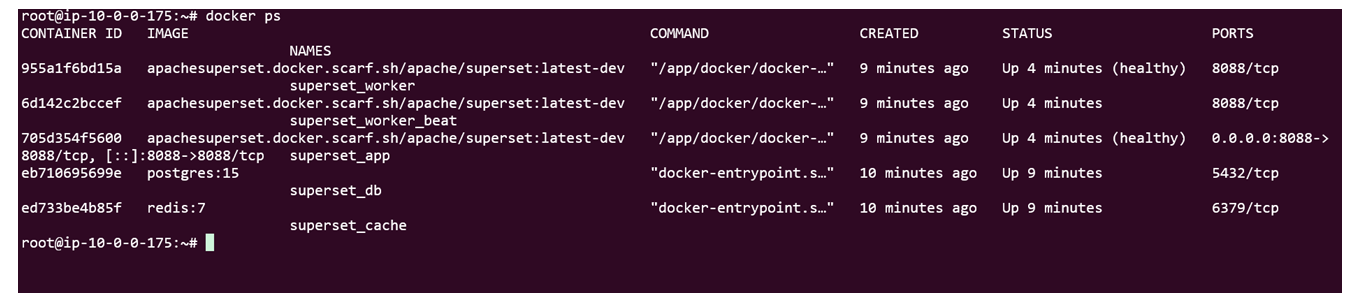
Shutting Down Superset
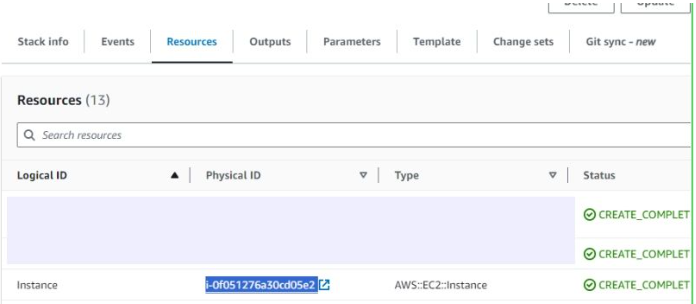
- In CloudFormation, click the link labeled "Instance" in the "Resources" tab to open the EC2 instance.
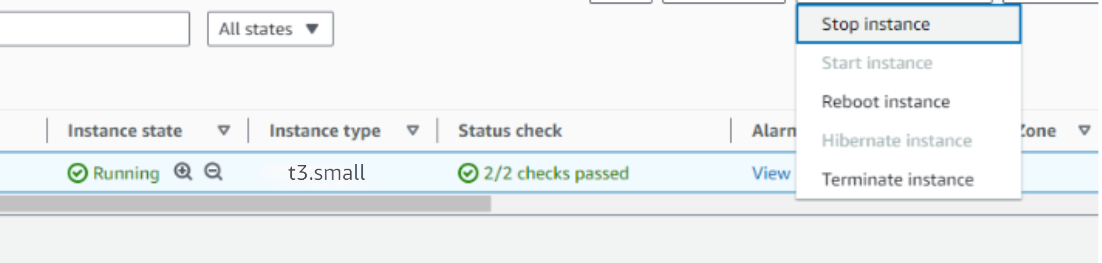
- Stop the Superset instance from the Instance state dropdown. You can restart it later as needed.
Remove Superset
Delete the CloudFormation stack from the AWS Management Console under "CloudFormation Stacks" by clicking "Delete".
Upgrades
When a new version is available in AWS Marketplace, remove the previous deployment after backing up necessary server data, and relaunch with the new version.
Troubleshoot
- If you face vCPU quota limits, request an increase: How to increase AWS quota.
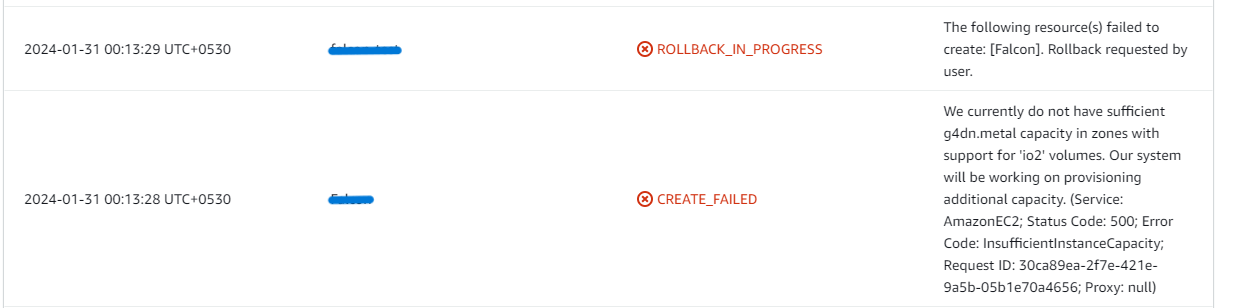
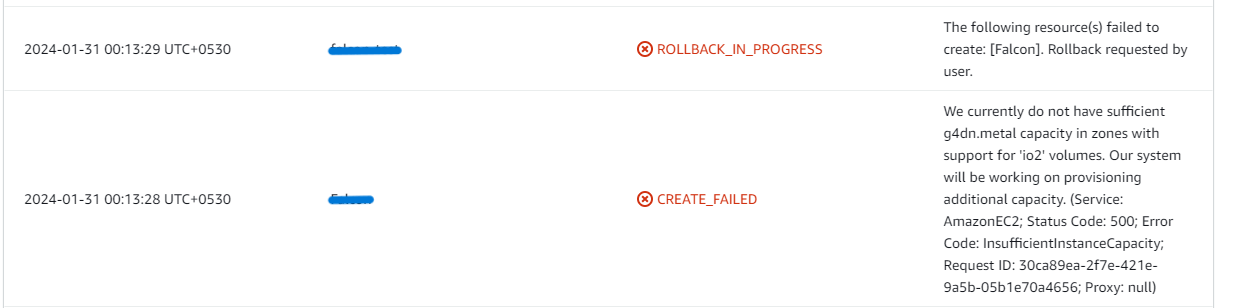
- If you face insufficient capacity errors while creating the stack, try another region or time.
- If the dashboard is temporarily inaccessible, wait 5–10 minutes and retry.
Check whether the instance storage is full.
- Log into the server and run:
df -h
- If the root volume is between 90–100%, resize the EBS volume (per AWS docs), then reboot and restart the service.
Conclusion
The Meetrix Superset Deployment Guide helps you integrate Superset into your AWS environment. Whether you're a DevOps engineer, data architect, or IT leader, this guide provides step-by-step instructions for a secure and scalable setup.
Technical Support
Reach out to Meetrix Support (aws@meetrix.io) for assistance with Superset issues.
